Hoverboards are very popular, but few individuals understand their technology. No question, the device has been one of the hottest gift items during the holiday season. Still, the casual observer wants to learn more about the product’s design, sometimes known as a self-balancing scooter, as the sensor helps the rider stay balanced. Together, let’s try to understand how a hoverboard works.
Introduction
What is a hoverboard? Well, it is a two-wheeled, portable electrical device. Many people are familiar with the gyro hoverboard from the 1980s film classic, Back to the Future. If you’re still unfamiliar and want to know what a hoverboard looks like? Then, think of a skateboard attached on the top of two wheels as the frame pivots the center of gravity. However, today’s devices do not levitate like the one used by Marty McFly. Instead, a person rides on the wheels, which makes traveling more fun and exciting.
Let’s take a closer look at the inside of a hoverboard.
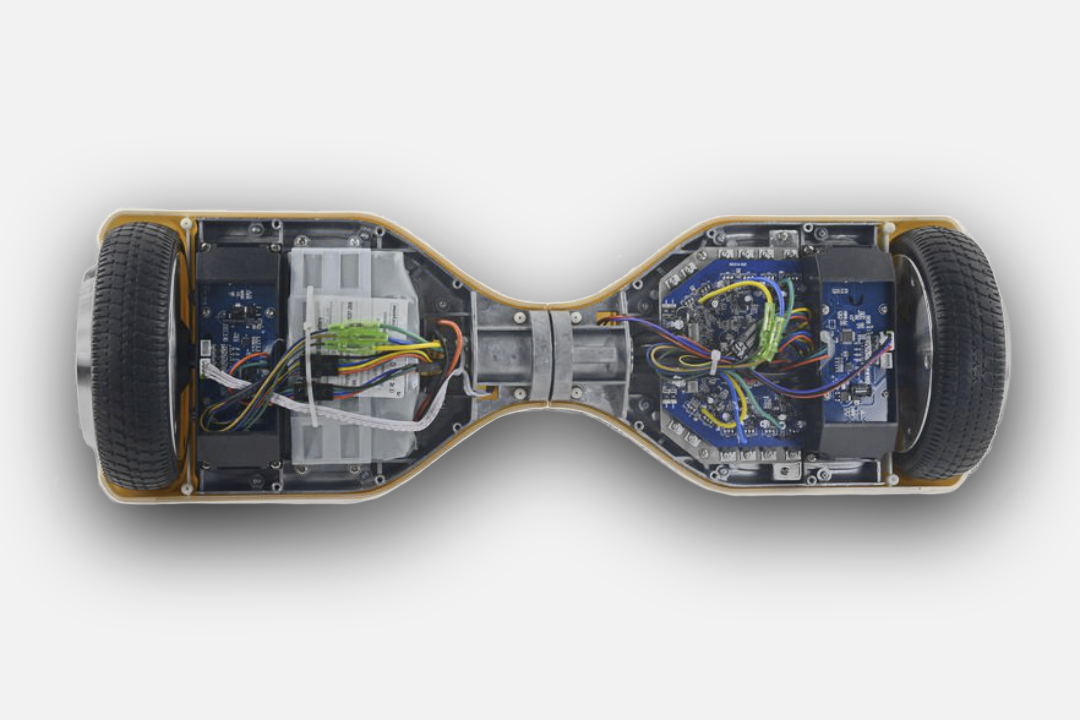
What’s Inside a Hoverboard?
Owners of hoverboards are curious in their own nature. Many would love to open the inside of one and see how it actually operates. Often, this is where all their answers lie. We will learn how a hoverboard works to keep a person upright during their ride. Usually, it is a combination of motor and other machine parts that keep the device propelling and the rider onboard simultaneously.
Most hoverboards consist of:
- The battery pack
- Gyroscope
- The logic board
- Wheels and motor
Each component works in unison to bring power to move about at various amounts of speed. Plus, the device’s design allows each user to tilt their body at multiple angles while still maintaining an upright position on the hoverboard. Most devices can travel at a rate of speed between 6-12 miles per hour. There are quite a few mechanical parts that define how a hoverboard works. From the sensor technology to the motor itself, there is a lot to cover.
Here are the basic responsibilities for each of the above mentioned main components:
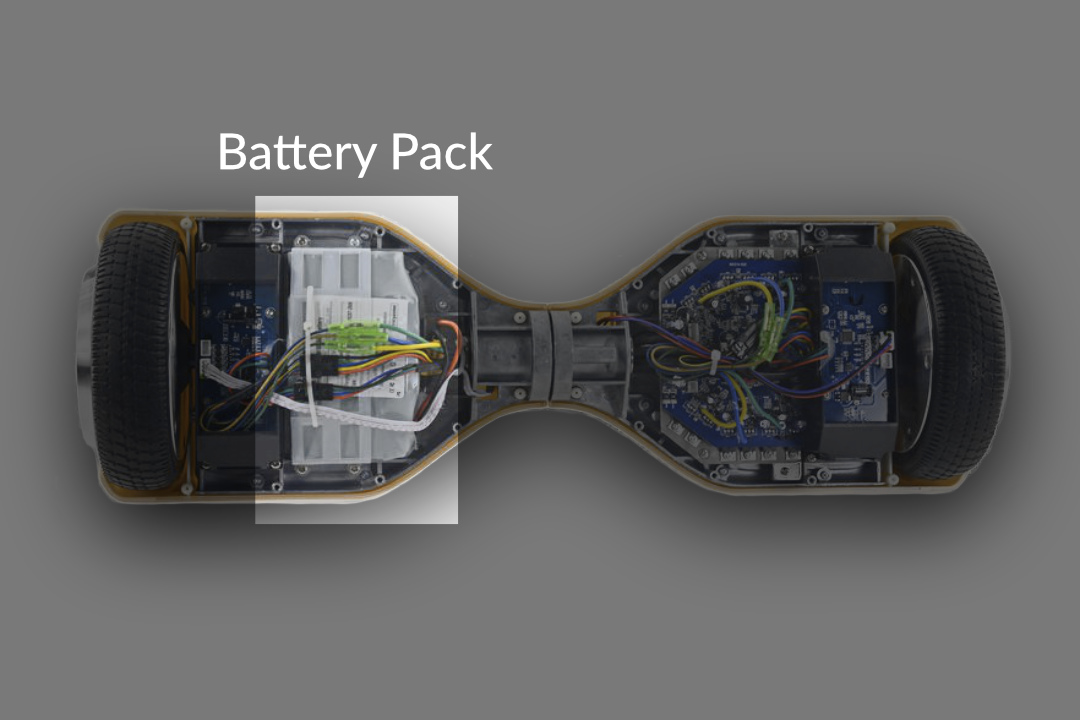
The Battery Pack
The power generated by the hoverboard comes directly from the pack of built-in batteries. The majority of the devices use a lithium battery as they are lightweight and offer higher density than other types of batteries on the market. Lithium batteries will lose power at a slower rate than their competition.
This comes in handy if you have not used your hoverboard regularly. All you need to do is charge up the lithium battery before getting on the device. Other advantages in using a lithium battery power include gaining more mileage per one charge period.
However, hoverboards must remain a lightweight device at all times, or you will lose the efficiency to gain the best mileage possible. Usually, the extra weight will diminish the device’s ability to maintain speed when trying to climb different slope ranges and terrains in your travels.
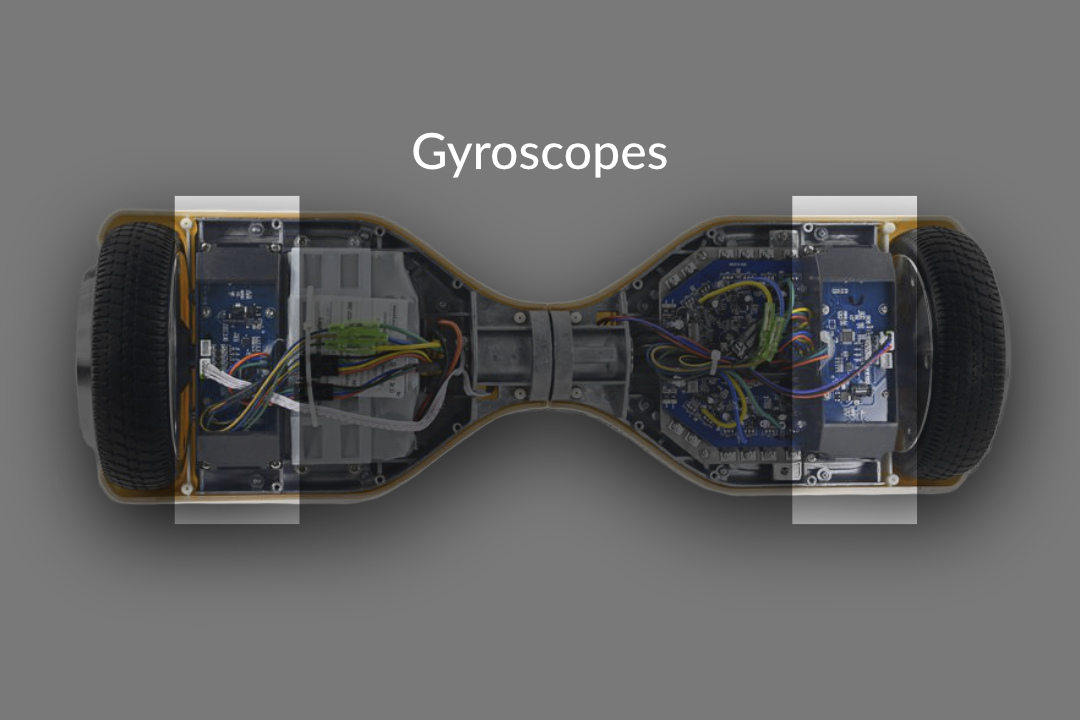
Gyroscopes
The gyroscope’s role is to help adjust the hoverboard’s tilt angle, which helps a rider maintain balance. How is this accomplished? Well, each wheel sends a separate message that details the required speed and tilt angle needed to maintain the proper balance for the ride. Where is this message going? The gyroscope has a direct line of communication with the device’s logic board.
However, this transmission line can go offline from time to time. Often, this is a sign that your hoverboard needs recalibration. Have no fear, as all this means is a reset of the device’s gyroscope back to its original setting.
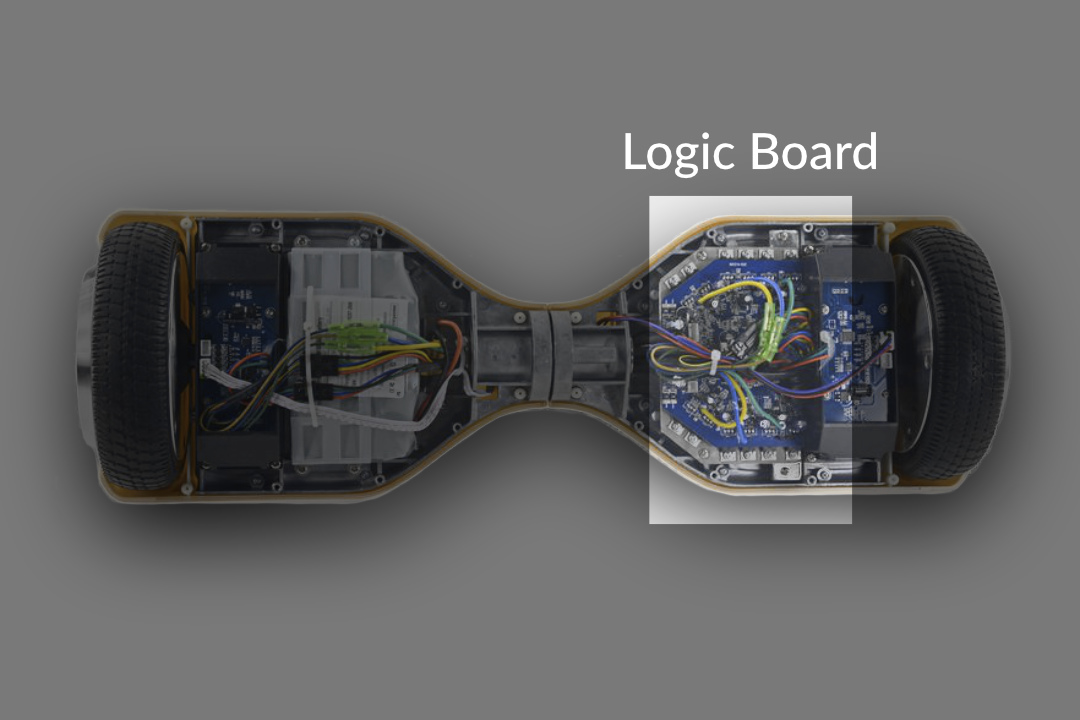
The Logic Board
The logic board regulates the power output to each wheel. Many hoverboard owners believe the logic board acts like a computer’s processor for their device. Why? Because, it controls every aspect of the hoverboard. Movement is based on the information provided by the gyroscope. The main job of the logic board is to decipher this information before allowing the hoverboard to move forward. Some of the more common commands given by the logic board includes reacting to the riding mode selected, LED lights, variation in speed levels and power consumption. Each command plays a vital role in the smoothness of your ride.
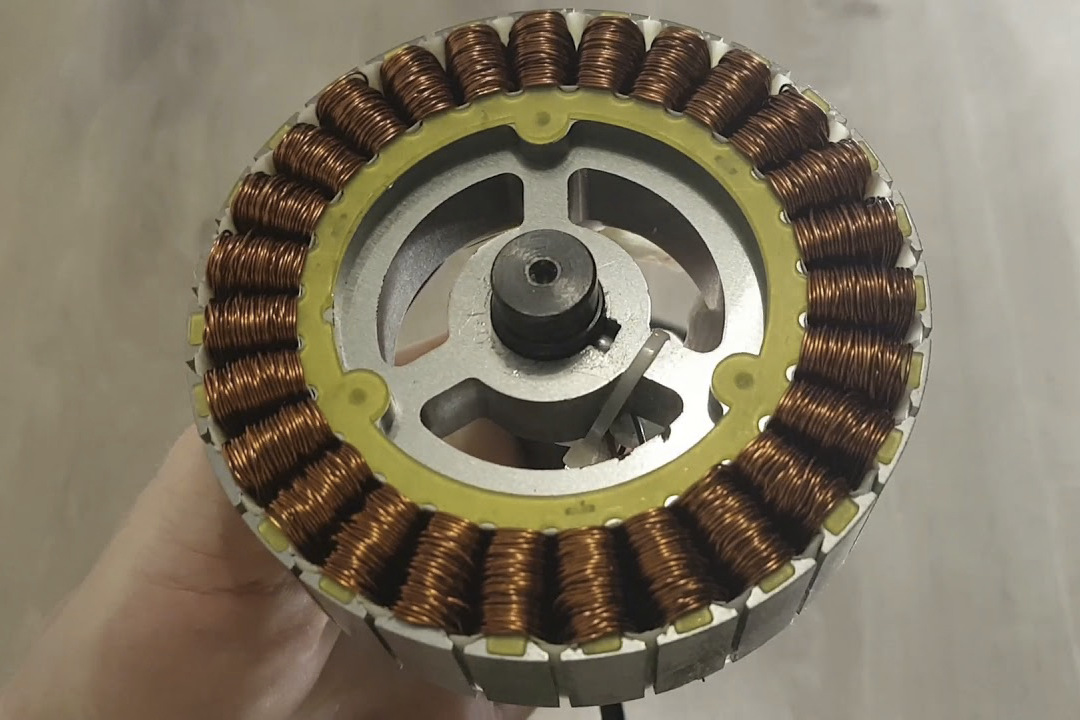

Wheels and Motor
In order to remain upright and balanced on your hoverboard, your wheels and motor must work together simultaneously. Most devices have two electric motors which use magnetic fields to turn the wheel, as each is responsible for either the right or left wheel. Their primary purpose is to regulate the acceleration level of each wheel. This will allow them to move independently of one another when needed. Think of this movement the same way as automobile wheels, who need to act on their own at times. This helps the vehicle to turn in either direction.
Each wheel has its own group of speed sensors that read the level of speed generated and tilt sensors to measure the angle required while you’re riding the device on the hoverboard. All of this information gathered and sent via a carrier (gyroscope) to the logic board.
The Technology Inside The Foot Pads
When you step onto a hoverboard, you’re standing on two highly-sensitive foot pads that are activated by any sort of movement. Each foot pad has two switches (front and back), infrared light, and an infrared sensor. The connection between the infrared light and sensor is ultra-important. When the sensor detects the light, then the logic board will keep the motor at a standstill. However, if you’re leaning forward on the hoverboard and putting pressure on the front of the foot pad, then the logic board will begin powering the motor for travel.
Once the switches are activated, then the hoverboard wheels will accelerate in either direction. The front right switch will accelerate the hoverboard forward. The back left switch will accelerate the hoverboard backward. If you tilt your right foot forward and your left foot backward, the right front switch activates, telling the right wheel to accelerate forward, and the left wheel will go back, causing you to turn.
Remember the more significant the tilt angle of your body, the wheel’s sensors will make the necessary adjustments in keeping the hoverboard balanced for a smoother ride. The rate of acceleration is dependent upon the angle of your lean. This is made possible by the information gathered and passed on by the gyroscope to the device’s logic board.
Wrapping Up
Keep in mind, this is a beginner’s guide to the inner workings of a hoverboard. Hopefully, the information provided helps you to gain a better perspective of the device. And for some, it will pique your interest to gain further knowledge on how a hoverboard works.
This content’s goal is to gain a basic understanding of the hoverboard, which helps you have a fun, safe ride on the device. From our perspective, it is all about enhancing your riding experience.
Keep in mind that no two hoverboards are the same. Each offers different functions that will make your traveling experience to be a bit bumpy at first. Thankfully, the basic functions are similar, making for adapting from one hoverboard to another a smoother transitional process.